Add alternating background color along the y-axis. The geom takes default
aesthetics odd and even that receive color codes. The codes
would preferably be in the 8-hex ARGB format to allow for transparency if
the geom is meant to be used as visual background.
geom_stripes( mapping = NULL, data = NULL, stat = "identity", position = "identity", ..., show.legend = NA, inherit.aes = TRUE )
Arguments
| mapping | Set of aesthetic mappings created by |
|---|---|
| data | The data to be displayed in this layer. There are three options: If A A |
| stat | The statistical transformation to use on the data for this layer, as a string. |
| position | Position adjustment, either as a string, or the result of a call to a position adjustment function. |
| ... | Other arguments passed on to |
| show.legend | logical. Should this layer be included in the legends?
|
| inherit.aes | If |
Examples
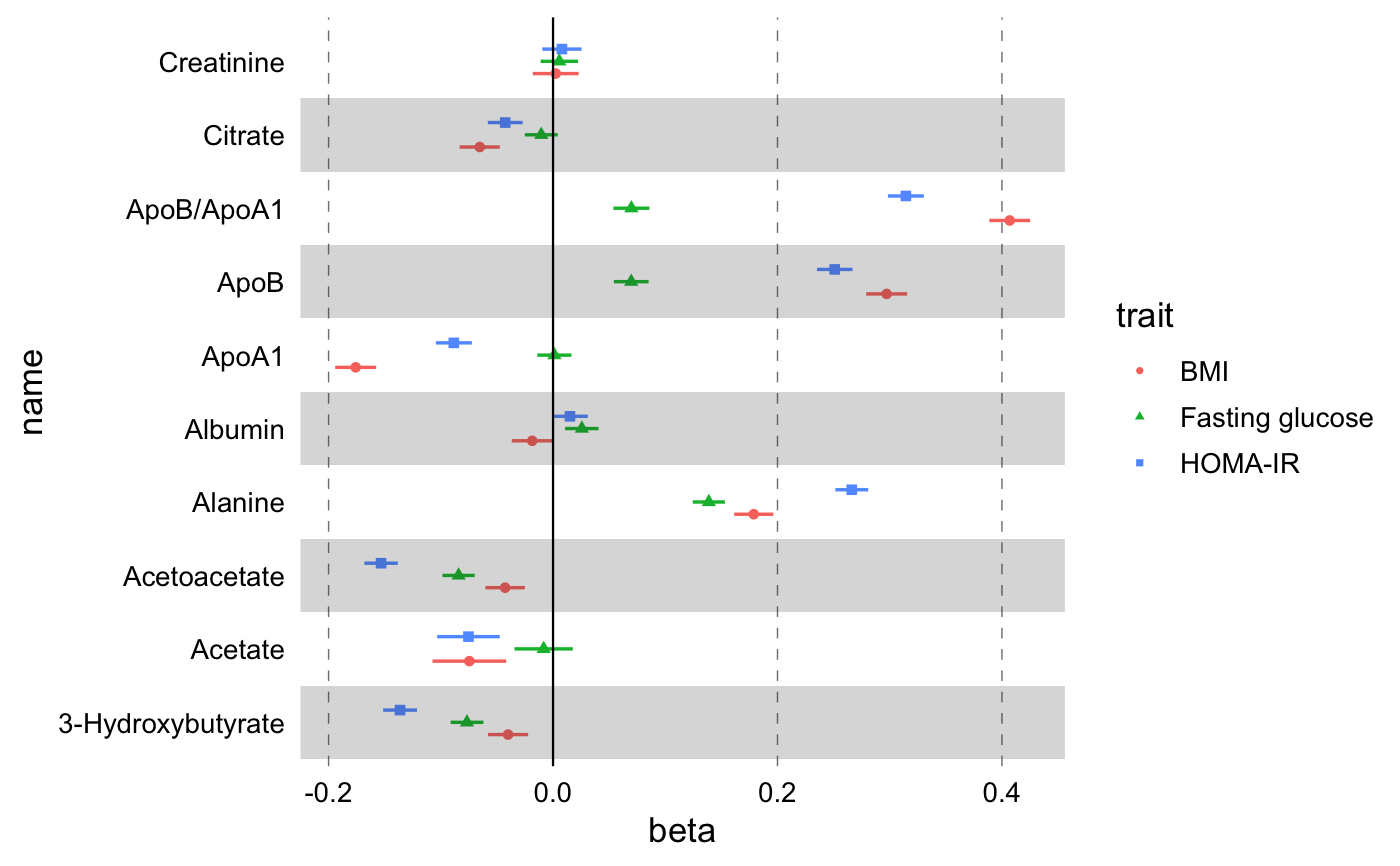
library(ggplot2) library(magrittr) df <- # Use built-in demo dataset df_linear_associations %>% # Arrange by name in order to filter the first few biomarkers for more # than one studies dplyr::arrange(name) %>% # Estimate confidence intervals dplyr::mutate( xmin = beta - qnorm(1 - (1 - 0.95) / 2) * se, xmax = beta + qnorm(1 - (1 - 0.95) / 2) * se ) %>% # Select only first 30 rows (10 biomarkers) dplyr::filter(dplyr::row_number() <= 30) %>% # Add a logical variable for statistical significance dplyr::mutate(filled = pvalue < 0.001) g <- ggplot(data = df, aes(x = beta, y = name)) + # And point+errorbars geom_effect( ggplot2::aes( xmin = xmin, xmax = xmax, colour = trait, shape = trait, filled = filled ), position = ggstance::position_dodgev(height = 0.5) ) print(g)# Add custom theme, horizontal gray rectangles, vertical line to signify the # NULL point, custom color palettes. g <- g + # Add custom theme theme_forest() + # Add striped background geom_stripes(odd = "#33333333", even = "#00000000") + # Add vertical line at null point geom_vline( xintercept = 0, linetype = "solid", size = 0.4, colour = "black" ) print(g)